The requirements of the IP Code for ingress protection are an important consideration for electricians involved in the design of electrical installations. The IP Code involves the ingress protection of barriers, enclosures, wiring systems and accessories, with the resultant implications for safety.
Requirements of BS 7671
Regulation 132.5.1 declares that the design of electrical installations must take into account the environmental conditions to which they will be subjected. Regulation 132.7 asserts that the choice of the type of wiring system and methods of installation must include consideration of:
- the nature of the location
- the nature of the structure supporting the wiring
- accessibility of wiring to persons and livestock
- voltage
- the electromechanical stresses likely to occur due to short-circuit and earth fault currents
- electromagnetic interference
- other external influences (e.g. mechanical, thermal and those associated with fire) to which the wiring is likely to be exposed during the erection of the electrical installation or in service
Regulation 133.3 states essentially that electrical equipment must be suitable for its location. Where necessary to ensure its suitability, electrical equipment may require adequate further protection to be provided as part of the completed electrical installation. Regulation 512.2.2 refers to ‘appropriate additional protection’ from external influences.
Section 522 requires that the installation method selected must be such that protection against the expected external influences is ensured in all appropriate parts of the wiring system. Particular care must be taken at changes in direction and where wiring enters into equipment.
Regulations 522.1 to 522.15 cover the following external influences:
- ambient temperature (AA).
- external heat sources.
- presence of water (AD) or high humidity (AB).
- presence of solid foreign bodies (AE).
- presence of corrosive or polluting substances (AF).
- impact (AG).
- vibration (AH).
- other mechanical stresses (AJ).
- presence of flora and/or mould growth (AK).
- presence of fauna. (AL).
- solar radiation (AN) and ultraviolet radiation.
- seismic effects (AP).
- movement of air (AR).
- nature of processed or stored materials (BE).
- building design (CB).
Classification of External Influences
Appendix 5 of BS 7671 lists the classification and codification of external influences. Each codification is designated by a code comprising of two capital letters and a number.
The first letter of the code is related to the general category of external influence. The second letter concerns the nature of the external influence. The number pertains to the class within each external influence.
For example: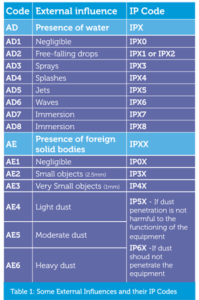
Environmental code AD4
A = Environment
D = Water
4 = Splashes
The IP Code for ingress protection
The requirements of the IP Code are given in BS EN 60529, ‘Degrees of protection provided by enclosures’.
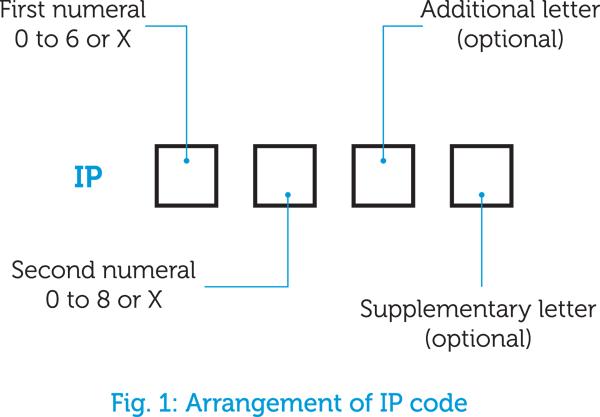
The arrangement of the IP Code is shown in Fig. 1 and its application is illustrated in Table 1 (Table 1 is a condensed extract from Appendix 5 of BS 7671)
When one of the numbers in the code has the letter X in place of the first or second numeral (eg. IPX4 and IP4X), this indicates that the particular characteristic is not applicable to the product. It is also used in standards to indicate that, for the range of products covered, such protection is not required.
For the code AD4 given above, equipment and accessories are required to have at least the degree of protection of IPX4.
Additional letter (optional)
An additional letter can be used to denote enhanced personal protection.
- A protection against access with the back of the hand
- B protected against access with a finger
- C protection against access with a tool
- D protection against access with a wire
(extracted from Table B2 in IET Guidance Note 1)
Supplementary letter (optional)
A supplementary letter can be used to denote supplementary information from the product standard.
- H high-voltage apparatus
- M tested for harmful effects due to ingress of water when the movable parts of the equipment are stationary
- S tested for harmful effects due to ingress of water when the movable parts of the equipment (eg. the rotor of a rotating machine) are stationary
- W suitable for use under specified weather conditions
(extracted from Table B3 in IET Guidance Note 1)
IP Classification Testing
IP classification testing is normally carried out in accordance with the BS EN 60529 standard. The test for IP 2X involves pressing a standard 12mm diameter test finger with a force of 10 N, and a 12.5 mm sphere with a force of 30 N, against all openings in the enclosure. For acceptance, the sphere must not fully enter the enclosure and there must be a satisfactory distance between the test finger and any dangerous live parts and moving parts.
The test for IP4X involves pressing a standard test probe, in the form of a 1mm steel wire, against all openings in the enclosure with a force of 1N. For acceptance, the probe must not enter the enclosure.
The test for IPX4 requires exposing the enclosure to water spray from an oscillating tube, with each spray nozzle giving a flow rate of 0.07 l/minute for 10 minutes. Alternatively, a standardised spray nozzle, producing a spray of 10 l/minute, may be used. If this spray nozzle is used, the exposure time is 1minute/m2 for a minimum of five minutes.
Summary
It is important to establish the environment in which an electrical installation is to be installed then to select the correct IP-rated equipment to satisfy the requirements of BS 7671.
Source: https://www.voltimum.co.uk/articles/external-influences-and-ip-code




